PAPERS
Journal papers etc relevant to this collection
 Cardiovascular fluid dynamics: a journey... Cardiovascular fluid dynamics: a journey... |
 Fluid-structure interaction study of... Fluid-structure interaction study of... |
 Blood flow and vessel mechanics in a... Blood flow and vessel mechanics in a... |
PATENTS
Patents added to this collection
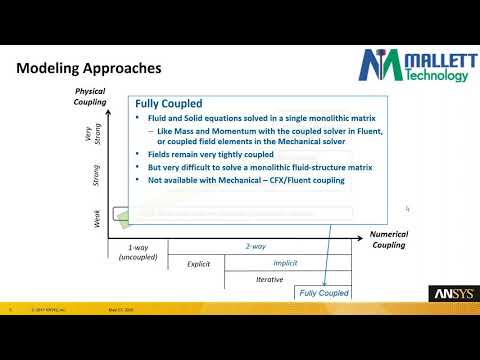
RECENT VIDEOS
Videos uploaded by others in other areas
DISCUSSIONS
Curated By
Rashu Raj
I am an ambitious pre-final year undergraduate student pursuing an integrated M.Tech program in Aerospace Engineering at the Indian Institute of Technology Kharagpur. With a strong passion for problem-solving and a collaborative mindset, I am constantly seeking opportunities to contribute to the...
View ProfileContributors
People who have contributed to this collection
Workshops and Short Courses
No short courses scheduled yet
Request a topic of interest.
A short course for this topic has not been currently scheduled. You may request a topic of interst that you would like this instructor to cover in the short course. Please follow this instructor to be notified when any of his or her short courses come online.
BOOKS
Books relevant to this collection
DOCUMENTS
Documents uploaded to this collection
 Blood flow simulation in carotid arteries with... Blood flow simulation in carotid arteries with... |
 Cardiovascular Fluid Mechanics... Cardiovascular Fluid Mechanics... |
 Carotid Artery CAD File (2 Body)... Carotid Artery CAD File (2 Body)... |
 BTP I_Report... BTP I_Report... |
 BTP II_Report... BTP II_Report... |
PAPERS
Journal papers etc relevant to this collection
 Cardiovascular fluid dynamics: a journey... Cardiovascular fluid dynamics: a journey... |
 Fluid-structure interaction study of... Fluid-structure interaction study of... |
 Blood flow and vessel mechanics in a... Blood flow and vessel mechanics in a... |
ACTIVITIES
List and page updates
BOOKS
Books relevant to this collection
PATENTS
Patents added to this collection
EXTERNAL RESOURCES
Webresorces for this collection
 FSI simulation archive files (CFD)... FSI simulation archive files (CFD)... |
 CFD Tutorial of 3D Bifurcating Artery... CFD Tutorial of 3D Bifurcating Artery... |